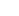Ayia Roumeli
This is one name for two different settlements, the old and the new (inside and out) – Ayia Roumeli. The old village is located at the exit of the Samaria Gorge, at what is, in essence, the end of the National Park and was abandoned after a great flood in November 1954. There are still the old houses there, some of which have begun to be renovated, and various churches, the main one dedicated to the Holy Trinity in the area of the settlement’s cemetery, south beyond the village towards the sea. The new settlement began to be organize after 1957 on the west bank of the river, which also runs through the gorge. It was extended after the 1970s on to the coast, where there is a small harbor. Except for on foot, by going through the Gorge or along the old cobbled footpath parallel with the coast, Ayia Roumeli is accessible only by sea. On the site of the village, archaeologists discovered the old cemetery of the ancient town of Tarras, the ruins of which exist mainly on the east bank of the river. Above the settlement lies the ‘Koules’, a Turkish fort built between 1866 and 1869, but evidently with a former Venetian period, since inside there is an old church. Recently an access path has been constructed which starts at the medical centre and the ruins of the Temple of Apollo. As it is quite steep, perhaps a preferable ascent is the old footpath which begins on the immediate left, just after crossing the bridge at the entrance of the old village, after the cemetery. Also in the new village there is the church of the Dormition of the Mother of God, built over the ruins of an Early Christian basilica for which were used ancient building materials from a temple, probably dedicated to
Apollo of Tarra. In front of this ruin, on the other side of the road, can bemade out, the site of a Roman structure where a centre of handicraft production of glass pots was discovered, together with a mass of discarded glass, which is at present exhibited in the Archaeological Museum of Hania. Unfortunately, the whole site has not been systematically excavated with only superficial surveys carried out, such as the one which resulted in the discovery of the Romanworkshop.
Today, the seaside settlement consists mainly of a tourist resort for the gorge walkers with small hotels, eating-places and connections by sea with the harbors of Souyia, Paleohora and Hora Sfakion.


















 Botanical
Botanical
 Culinary
Culinary
 Geology
Geology
 Hiking
Hiking
 Historical
Historical
 Village experiences
Village experiences
 Sports activities
Sports activities